Ovarian Cysts
- Home
- Ovarian Cysts
Get an Appointment
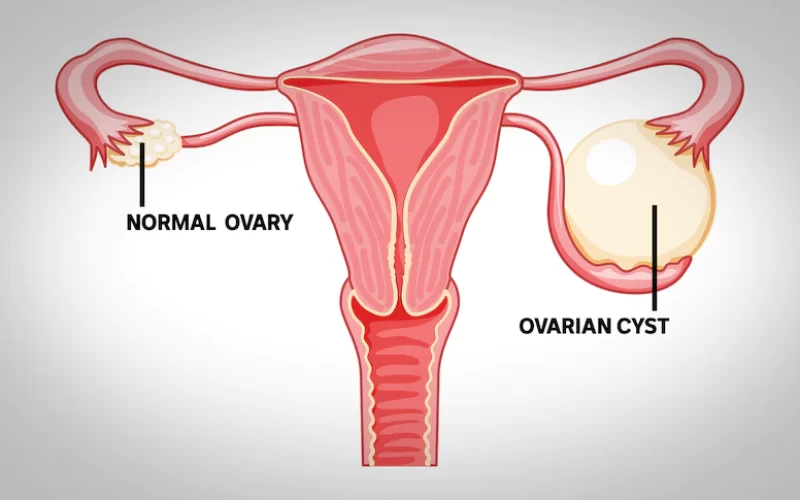
What are ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside an ovary. They are relatively common and can occur at any age, though they are most frequent during a woman’s reproductive years. Most ovarian cysts are harmless, cause no symptoms, and resolve on their own within a few weeks or months. However, some cysts can grow large, cause pain, or lead to complications that require medical attention.
Types of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts can be classified into several types, the most common being:
- Functional cysts – The most common type, which develops as part of the normal menstrual cycle, including follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts.
- Dermoid cysts – Contain tissue such as hair, skin, or teeth, as they form from embryonic cells.
- Endometriomas – Caused by endometriosis, where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus and attaches to the ovary.
- Cystadenomas – Develop from the surface of the ovary and can be filled with watery or mucous material.
Causes of ovarian cysts
- Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle.
- Endometriosis, which can lead to cyst-like growths on the ovaries.
- Pregnancy, where a cyst may form to support the early stages until the placenta develops.
- Certain fertility treatments that stimulate ovulation.
Frequently asked questions
Most ovarian cysts do not affect fertility, especially functional cysts that resolve naturally. However, cysts caused by conditions like endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can impact ovulation and make it harder to conceive.
No. Many cysts are painless and go unnoticed. Pain usually occurs when a cyst is large, ruptures, or causes twisting of the ovary.
While ovarian cysts often cannot be prevented, maintaining hormonal balance through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and routine check-ups can help reduce the risk of recurrence.
Ovarian cysts are usually single or few fluid-filled sacs, whereas PCOS involves multiple small cysts on the ovaries along with hormonal imbalances and irregular cycles.
